Acid Capture Elution (ACE) Method For Mitigating Drug Interference in ADA Assay- Biochemistry, molecular biology
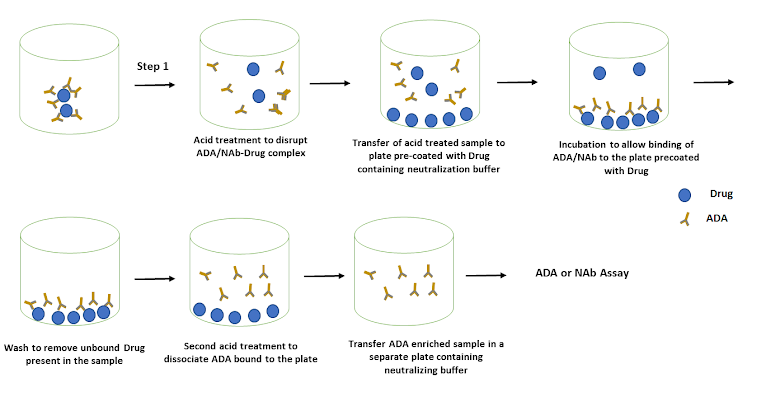
Acid capture elution (ACE) is a plate-based method for reducing the drug interference in the ADA (Adenosine deaminase) assay. It is used for the purification and isolation of specific nucleic acids, such as DNA or RNA, from a complex mixture. This method utilizes weak organic acids (Glycine, Acetic acid) to dissociate the drug-ADA complex.
- The sample is neutralized and allowed the bind the plate coated with the drug.
- After the ADA is captured, the plate is washed to remove any unbound drug present in the sample.
- The second acid treatment is used to elute the ADA bound to the plate.
- The ADA sample is transferred, neutralized with Tris-HCl base, and processed in the ADA detection assay.
Procedure:
1) Binding (Coating of the plate with a drug):
Maxisorp ELISA Nunc plate is widely used for coating the plate that would be used for the capture of ADA. For the optimization of drug concentration, test different concentrations of drug (0.5, 1.0, 5.0 ug/ml, and 10 ug/ml) and choose the concentration that provides higher tolerance and sensitivity. Incubate the drug in the high binding plate for one to two hours. Wash the plate and proceed to the next step.
2) Acid Treatment Dissociate ADA-Drug Serum Sample:
The addition of the in the sample dissociates the ADA-Drug complex present in the sample. The type, strength, volume of the acid are important variables that need to be evaluated. The polyclonal
antibodies present in the clinical samples have different affinities, therefore, the sufficient strength/volume of acid needs to be used for efficiently dissociating the ADA-drug complex.
300 mM acid, 600 mM acetic acid, 1 M Glycine have been commonly used acids in the ACE method. Usually, samples are diluted at 1:10 in the weak acid and incubated for 15 minutes.
3) Neutralization and Capture of ADA:
Next, 90.0 ul of acid-treated sample is transferred to the plate precoated with the drug, and a sufficient volume of 1M Tris HCl is added to bring to approximately pH 7.Incubate the neutralized sample for approximately 90-120 minutes and allow the ADA to bind to the drug adsorbed in the plate. After incubation, wash the plate using a plate washer to remove the unbound drug present in the sample.
4) Acid Elution of ADA
This acid treatment is used to dissociate or elute the ADA that is captured in the plate. Practically, the type/strength of acid that is used in the first acid dissociation (Step 2) may be used. It would sufficiently dissociate the ADA captured in the plate coated with the drug. As with the previous acid dissociation step, the samples are incubated with acid for 15 minutes.
After incubation, the samples are transferred into a new plate and neutralized using 1 M Tris-HCl. The neutralized samples are processed in the downstream ADA detection assay.
Comments
Post a Comment